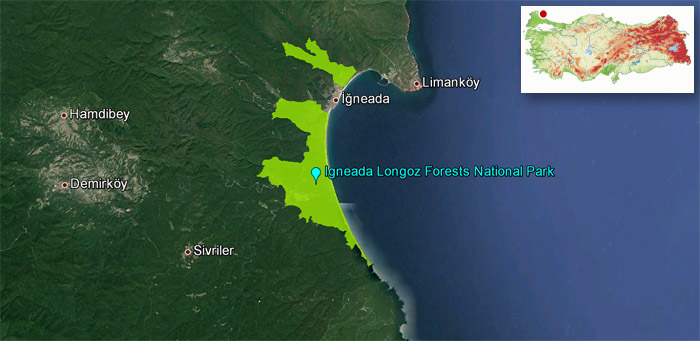
At the northern most tip of the Marmara Region, the last shore to be washed by the waters of the Black Sea, Igneada Longoz Forests National Park is a hidden Garden of Eden among the dark green forests.
The Longoz forests which are completely covered with water during winter and spring has a floristic composition of mixed forest trees of 8-15 meters tall. Since the alluvial soils have more intensive micro-organism activities, the forests and the other plants in this region start vegetation earlier than the other plants. The protection of the habitat of these forests has crucial importance. Because, these forests are not only a rare natural value for Turkey but also for Europe.
Preserved on a national scale and the scale of the most important European floodplains (Longoz) forests in the region of the Igneada (İğneada), the region contains many different ecosystems and different habitats for animal species are high quality. Many fish species due to habitat area and fish production potential of hunting tourism, botanical tourism thanks to its biological diversity, bird watching, nature photography and water sports, such as one of the areas that have high potential for many recreational activities.
The area is defined as a National Park on 2007. The lakes within the borders of Igneada are famous with its multiple species of fishes and oxygen rich atmosphere. Although Igneada Longoz Forests National Park has seven lakes, the most important ones are Mert Lake, Hamam Lake, Erikli Lake and Saka Lake. The first lake “Mert Lake” is just about 12 km far away from the Bulgarian border. It is known that, in the lagoons of Igneada, in the lakes, on the wetlands and on the streams 30 different species of fish live. According to the the Berne Convention 8 species of fish are described as “species in need of protection”. These are Chalcalburnuschalcoides, Syngnathus abaster, Neogobiusfluviatilis, Aspius Aspius, Alburnoidesbipunctatus, Rhodeus Amarus, CobitisTaenia Chondrostoma Nasus. Mert Lake has the highest diversity of fish between those lakes. Hamam and Pedina Lakes can also be defined as an accommadation point for birds, wild ducks and swans coming from Bulgaria, Russia and from the Danube River.
Hamam Lake: This lake, 20 km south of Igneada, which is surrounded by forestland is 2 km to the Black Sea and 20 meters elevation from sea level. Its square measure is 19 hectares and the deepest point is 2,6 meters. The lake which is supplied by numerous streams from inside the forest transfers excess water into Bulanik (Bulanık) Stream through a channel in the Southeast. Perch and crayfish take an important place in the fauna of the lake.
Saka Lake Longoz: It is in the south of Igneada and was formed through the filling of Bulanik Stream. The lake has nearly 5 hectares of land with reed fields. This land is submerged in Spring and Autumn due to the increase in water levels and is a longoz found rare in Turkey and Europe. There are alders, witch elms, European ashes, oaks, hornbeams, common beeches, black poplars, willow trees, limes and walnut trees in the longoz. It was declared as a protected area in 1988.
Pedina Lake: This lake which is 25 km south of Igneada and 5 km west of Hamam Lake is fully in the forest like Hamam Lake. The square measure of the lake is 10 hectares. The lake which is supplied bu numerous streams from inside the forest and also by Pedina Stream transfers excess water into Bulanik Stream through a channel. Igneada region has a rich biological diversity and natural balance in the region was not disturbed. Approxtimately 670 plants exist in the region. Mammals such as deer, roe-deer, wild boar, wolf, fox, jackal, wildcat, weasel, mustelid, bat, otter and 194 bird species such as pygmy, cormorant, white-tailed eagle, lesser kestrel, grey-headed woodpecker, lizard, green lizard, copper skink, snake, turtle and insects such as butterfly and fish such as anchovy, monkey goby, wolfish, spirlin, narroe-snouted pipefish, bitterling, painted comber live in Igneada Longoz Forest region.
The Dupnisa Caves are excellent for an adventurous trek. Dupnisa about cave 4 million years since the formation of a large underground system, and continues to 2720 meter-long cave is said to be the second longest in Thrace (Trakya).
With its serene blue sea, bright sun and dramatic sky, Igneada Longoz Forests National Park is sure to satisfy your need to get close to nature.
The historical attractions include the castle ruins from the Genoese period, the Sivriler village where you can see the old houses that are thought to belong to the Thracians, and also the Thracian tombs.
Situated between the Hamam Lake and the Bulanik River, Aypolos district is interesting for the ancient mounds, the tumulus, the graves, in addition to the ruins of housing structures.
Internationally renowned for its ecological diversity and rare type of flooding forests, Longoz floodplains forest area is protected as a National Park. The forest area houses a rich variety of plants, trees, animals and birds as well as numerous water creatures living in its many lakes.